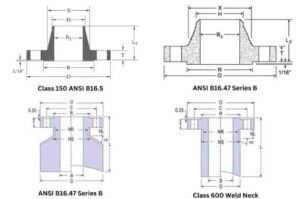
Flange dimensions are an important aspect of the industrial world, playing a pivotal role in connecting pipes, valves, and various equipment in piping systems. This guide provides comprehensive insights into flange dimensions, why they are standardized, and the specific details and standards that govern them.
Image Source: Texas Flange
The Significance of Standard Flange Dimensions
Flanges are practical components in numerous industries, serving the vital function of creating secure connections within piping systems. While the importance of standardizing flange dimensions may not be glamorous, it is undeniably essential for the seamless operation of these systems. Here’s why it matters:
- Streamlined Replacements: Standardized flange dimensions simplify the process of replacing flanges. Engineers and designers can specify a particular type and size of flange, knowing it will fit perfectly without compatibility issues.
- Safety Assurance: Flanges must contend with high pressures, extreme temperatures, and various fluids. Standard dimensions enable manufacturers to produce flanges that adhere to precise safety requirements, reducing the risk of accidents and failures.
- Effective Communication: Universal standards in flange dimensions foster a shared language among professionals in the field. This commonality minimizes misunderstandings and errors, enhancing the overall efficiency and reliability of piping systems.
Understanding Flange Dimensions
Flange dimensions are not arbitrary; they follow specific criteria and are categorized by types, sizes, pressure classes, schedules, and standards. Here’s a closer look at these parameters:
- Flange Type: Flanges come in various types, each tailored for particular applications. Common types include Welding Neck, Slip-On, Blind, Lap Joint, Socket Weld, and Threaded flanges. The choice of flange type depends on the specific requirements of the piping system.
- Size: Flange size is typically denoted in NPS (Nominal Pipe Size), and it refers to the diameter of the connected pipe. Flanges can range from small sizes (e.g., NPS 1/2) to much larger ones (e.g., NPS 60).
- Pressure Class: Flanges are classified into different pressure classes, which signify their ability to withstand various levels of pressure. Pressure classes vary from 150 to 2500, with the number corresponding to pounds per square inch (psi).
- Schedule: The schedule of a flange pertains to the thickness of the connected pipe. It is expressed as a schedule number (e.g., Schedule 40) and affects the pressure-carrying capacity of the flange.
- Standard: Flange standards provide guidelines for the design, dimensions, and materials used in flange construction. Prominent standards include ASME B16.5, ANSI/AWWA C110/A21.10, ANSI/AWWA C111/A21.11, and ANSI/AWWA C153/A21.53.
- Specification: In addition to standards, flanges must adhere to specific material and sealing face type specifications. For instance, flanges can be constructed from materials such as ASTM A105, which is well-suited for certain applications.
Flange Dimensions: The Details
Flange dimensions are specified according to their type, size, pressure class, and schedule. Here are the typical dimensions of Welding Neck flanges as per ASME B16.5:
- Size (inches): Ranging from 1/2″ to 60″.
- Outside Diameter (inches): Varies according to flange size.
- Thickness (inches): Corresponding to schedule and flange size.
- Bolt Hole Diameter (inches): Determined by flange size and pressure class.
- Number of Bolts Per Joint: Varies, with larger flanges generally requiring more bolts.
- Bolt Size (inches): Reflects flange size and pressure class.
It’s important to note that standardization is key, preventing compatibility issues and allowing for straightforward communication among industry professionals.
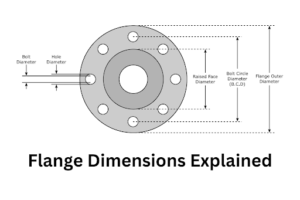 Image Source: Texas Flange
Image Source: Texas Flange
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are flange dimensions, and why are they important?
Flange dimensions refer to the specific measurements and standards used to design and manufacture flanges, which are important components in piping systems. These dimensions are essential for ensuring proper fit, safety, and communication in industrial applications.
How do I determine the right flange size for my piping system?
The flange size is typically determined based on the nominal pipe size (NPS) of the connected pipe. Select a flange size that matches the NPS of your pipe for a secure fit.
What is the significance of pressure class in flange dimensions?
Pressure class indicates a flange’s ability to withstand pressure. It is essential to choose a flange with a pressure class that matches or exceeds the system’s operational pressure.
How does the flange schedule affect the choice of flange dimensions?
The flange schedule corresponds to the thickness of the connected pipe. It impacts the flange’s pressure-carrying capacity. Select a flange with a schedule that aligns with your piping system requirements.
What types of flanges are commonly used, and when should I use each type?
Common flange types include Welding Neck, Slip-On, Blind, Lap Joint, Socket Weld, and Threaded flanges. The choice of flange type depends on the specific needs of your piping system, such as welding, sealing, or accessibility.
What are the key standards governing flange dimensions?
Prominent standards include ASME B16.5, ANSI/AWWA C110/A21.10, ANSI/AWWA C111/A21.11, and ANSI/AWWA C153/A21.53. These standards provide guidelines for flange design, dimensions, and materials.
Why is it important to specify a particular material, like ASTM A105, for flanges?
Material specifications, like ASTM A105, ensure that the flange is constructed from suitable materials for specific applications, offering corrosion resistance, strength, and other required properties.
What does “raised face” (RF) mean in flange dimensions?
A raised face (RF) is a default sealing face type specified in ASME B16.5. It refers to the raised portion around the flange’s inside diameter, which helps create a tight seal when connecting two flanges.
How do I choose the number and size of bolts for a flange connection?
The number and size of bolts depend on the flange size and pressure class. Refer to flange dimensions charts to select the appropriate bolt configuration for your specific application.
Can flanges of different standards and specifications be connected?
While it’s generally advisable to match flanges with the same standards and specifications, some variations may be compatible. Consult experts or resources for specific cross-standard connections.
Are there alternative options to flanges for connecting pipes and equipment?
Yes, alternatives like welding, grooved connections, or compression fittings exist. The choice depends on the application’s specific requirements and the materials being used.
Do flange dimensions vary for non-standard or custom flanges?
Flange dimensions can be customized to meet specific requirements, but these customizations must be well-documented and specified in the order.
Can flanges be used in applications beyond piping systems?
Yes, flanges find applications in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and petrochemical sectors, where secure and leak-resistant connections are essential.
What tools and resources can help me learn more about flange dimensions and applications?
You can explore educational courses, books, online guides, and the resources mentioned in this article to delve deeper into flange dimensions and their significance.
How do I ensure the safety and reliability of flange connections in my system?
Regular inspection, maintenance, and adherence to standards and guidelines are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of flange connections in any system. Consulting with experts is also advisable for complex applications.
Conclusion
Flange dimensions might not be the most glamorous topic in the world of industry, but they play a critical role in the efficient and safe functioning of piping systems. Standardization ensures that flanges seamlessly connect pipes and equipment, meeting safety standards while simplifying communication among professionals. By understanding the specifics of flange dimensions, engineers and workers in various industries can maintain reliable and safe piping systems, even if it’s not the most thrilling aspect of their work.
Resources for Further Information
For more in-depth information on flange dimensions and related topics, consider exploring the following resources:
- https://www.texasflange.com/products/flange-dims-weights/ansi-b16-5-forged-flanges/class-150/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flange
These resources offer valuable insights into the world of flanges and can provide additional context and guidance for those interested in this subject.